Errors in Measurement and Significant Figures
Errors in Measurement and Significant Figures: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Errors in Measurements, Systematic Errors, Precision of Measurement & Accuracy of Measurement etc.
Important Questions on Errors in Measurement and Significant Figures
Which of the following is the approximate change in the volume of a cube of side meters caused by increasing the side by
The number of significant figures for the three number are:
If the error in the measurement of radius of a sphere is then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be:
The density of a cube is measured by measuring its mass and length of its sides. If the maximum error in the measurement of mass and length are and respectively, the maximum error in the measurement of density will be
The percentage errors in the measurement of mass and speed are and respectively. The error in kinetic energy obtained by measuring mass and speed will be:
In a vernier calliper divisions of vernier scale coincides with divisions of the main scale (in which length of one division is ). The least count of the instrument should be (in ):
A certain body weighs 22.42 gm and has a measured volume of 4.7 cc. The possible error in the measurement of mass and volume are 0.01 gm and 0.1 cc. Then maximum error in the density will be
A certain body weigh 22.42 gm and has a measured volume of 4.7 cc. The possible error in the measurement of mass and volume are 0.01 gm and 0.1 cc. Then maximum error in the density will be
The length and breadth of a metal sheet areand respectively. The area of this sheet up to the correct number of significant figures is
Assertion : When percentage errors in the measurement of mass and velocity are and respectively, the percentage error in K.E. is .
Reason :
Assertion: When percentage errors in the measurement of mass and velocity are and , respectively, the percentage error in Kinetic Energy is .
Reason: (where is the kinetic energy, is the mass and is the velocity).
A student performs an experiment to determine the Young’s modulus of a wire, exactly long, by Searle’s method. In a particular reading, the student measures the extension in the length of the wire to be with an uncertainty of at a load of exactly . The student also measures the diameter of the wire to be with an uncertainty of . Take (exact). The Young’s modulus obtained from the reading is
A student performs an experiment for determination of . The error in length is and in time is and is number of times the reading is taken. The measurement of is most accurate for
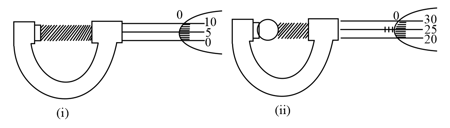
In a screw gauge, the zero of main scale coincides with fifth division of circular scale in figure (i). The circular divisions of screw gauge are It moves on main scale in one rotation. The diameter of the ball in figure (ii) is:
The side of a cube is measured by vernier callipers ( divisions of a vernier scale coincide with divisions of main scale, where division of main scale is ). The main scale reads and first division of vernier scale coincides with the main scale. Mass of the cube is . Find the density of the cube in appropriate significant figures.
The side of a cube is measured by vernier calipers ( divisions of a vernier scale coincide with divisions of main scale, where division of main scale is ). The main scale reads and first division of vernier scale coincides with the main scale. Mass of the cube is . Find the density of the cube in appropriate significant figures.
In Searle’s experiment, which is used to find Young’s Modulus of elasticity, the diameter of experimental wire is (measured by a scale of least count ) and length is (measured by a scale of least count ). A weight of 50 N causes an extension of (measured by a micrometer of least count ). Find maximum possible error in the values of Young’s modulus. Screw gauge and meter scale are free from error.
If division of main scale coincides with divisions of vernier scale. Given one main scale division is equal to units. Find the least count of the vernier.
Two objects and are of length and are determined with errors and respectively. Error in their total length and difference of their lengths are
What is the number of significant figures
